Morphology of flowering plants
Table of Contents
Floral Formula
Definition of Floral Formula
A floral formula can defined as the numeric and symbolic expression, which reveals the flower morphological characteristics by employing different symbols, letters, and figures. It is the conventional method accustomed to formulating the structure of the flower. It elucidates the information about the number of whorls and a relative relationship between each other.
Components
The floral formula uses discrete letters, signs and figures to represent the specific feature of the flower.
Letters used in Floral Formula
1.K: This letter denotes the sepals that form an outermost whorl called the calyx.

2. C: This letter represents the group of petals that constitute the second whorl called the corolla.
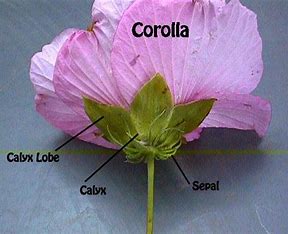
3. P: It is used to denote the tepals, which indicates the undifferentiated condition of the perianth members (sepals and petals).
4. A: It specifies the male reproduction part or stamens, which includes the filament and anther that all together makes up the third floral whorl known as androecium.
5. G: It denotes the female reproductive part, i.e. carpel, which includes the stigma, style and ovary that colloquially forms the innermost whorl called gynoecium.
6. Br: It represents the bracteate condition of the flower.
A plant having bracts is referred to as bracteate or bracteolate, while one that lacks them is referred to as ebracteate and ebracteolate, without bracts.
bracteate flowers: Flowers with bracts (a reduced leaf at the base of the pedicel) are called bracteate flowers. Bracts are small leaf-like structures found at a flower’s base. China rose, tulip, lily

7. Ebr: It indicates the ebracteate condition, in which a flower lacks bract.
8. Brl: It indicates the presence of bracteoles or represents the bracteolate condition.
9. Epik: It represents the presence of a secondary whorl surrounding the calyx called epicalyx.

10. Ebrl: It is used to indicate the absence of bracteoles or to represent the ebracteolate condition.
Symbols used in Floral Formula
- 0: It indicates the absence of a particular member in flower.
- ∞: It is generally used when the number of specific flower parts is more than 10.
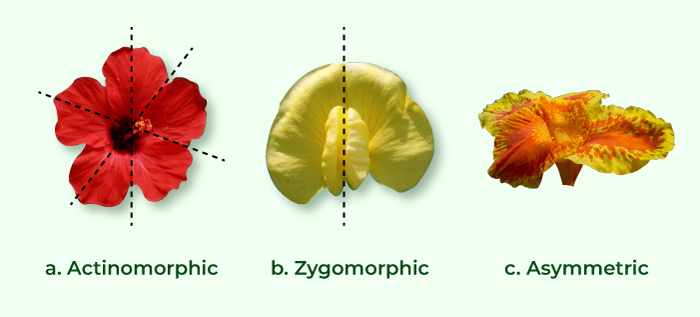
- ⊕: It indicates an actinomorphic condition.
- %: It denotes a zygomorphic condition.
- ⚥: It represents the bisexuality of flowers.
- ⚦: It represents the unisexual, staminate flower.
- ♀️: This represents the unisexual, pistillate flower.

Combination of Letters, Symbols and Numbers
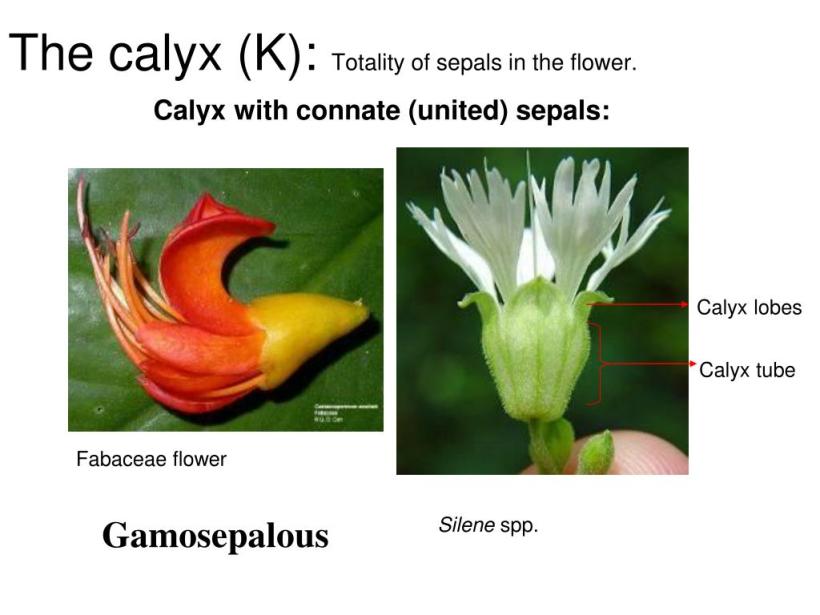
- K5: It shows the aposepalous condition, in which the five sepals are free.

- K(5): It shows the gamosepalous condition, in which the five sepals are united.
- C5: It represents the apopetalous condition or the presence of the five free petals.
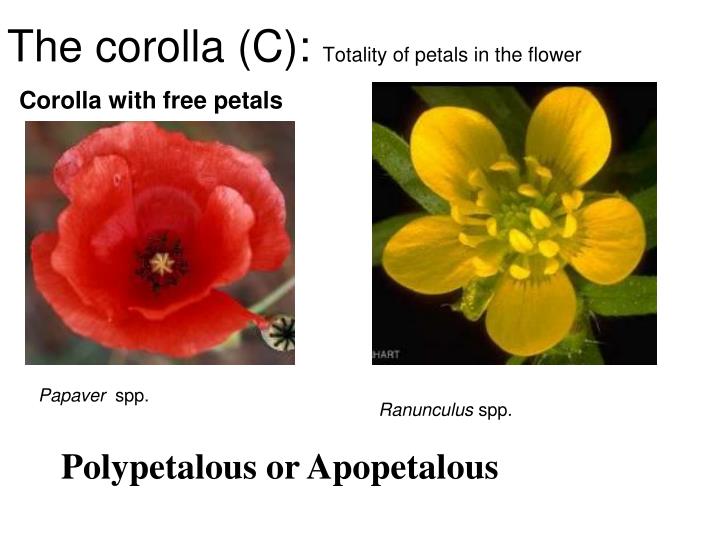
- C(5): It represents the gamopetalous condition or the presence of five fused petals.
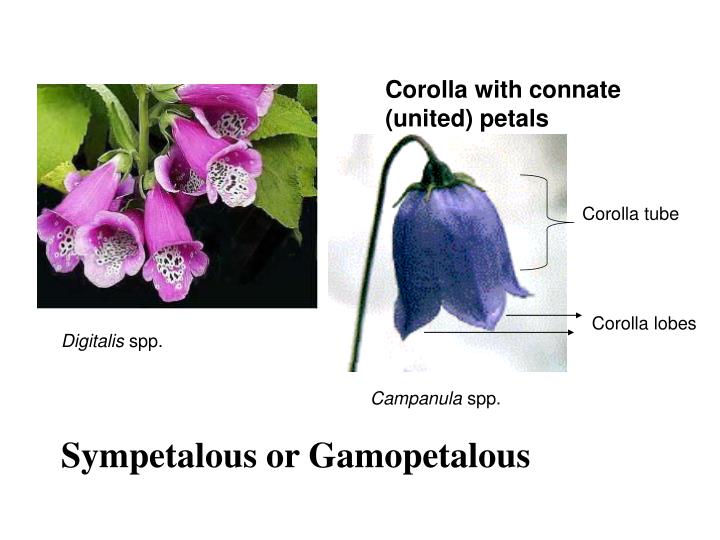
- Cx: It indicates corolla cruciform.
- A curve drawn over the letters P and A: It represents the epiphyllous stamens.
- A curve drawn over the letters C and A: It shows the epipetalous stamens.
- A3: It indicates the presence of three free stamens.
- A2+2: It indicates the presence of 4 free stamens, two in each whorl.
- A(9)+1: It represents the presence of diadelphous stamens (10 in number), in which nine stamens are fused in one whorl, and one stamen remains free.

- A0: Sterile stamen (staminode).
- G0: Sterile carpel (pistillode).
- G-: It represents the semi inferior ovary.
- A line over the letter G: It represents the inferior position of an ovary.
- The line below the letter G: It represents the superior position of an ovary.
- A curve over the letters G and A: It shows the gynostagium condition.
Floral Formula:
| Symbol | Description / Full form |
| Br | Bracteate condition |
| Ebr | Ebracteate condition |
| Brl | Bracteolate |
| Epik | Epicalyx |
| Ebrl | Ebracteolate |
| 0 (zero) | Absence of a particular whorl |
| ∞ | Indefinite number of floral parts in a whorl |
| ⊕ | Actinomorphic condition (radially symmetric) flowers. |
| % | Zygomorphic condition (bilaterally symmetric) |
| K | Calyx (Sepals) |
| C | Corolla (petals) |
| P | Perianth (tepals) |
| A | Androecium (stamens) |
| G | Gynoecium (carpels) |
| ⚥ | Bisexual flower |
| ⚦ | Unisexual, staminate flower |
| ♀️ | Unisexual, pistillate flower |
| K5 | Five sepals, aposepalous |
| K(5) | Five sepals gamosepalous |
| C5 | Five petals, apopetalous |
| C(5) | Five petals, gamopetalous |
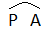 | Epiphyllous stamens |
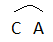 | Epipetalous stamens |
| A3 | Three stamens free |
| A2+2 | Stamens 4, 2 whorls |
| A10+1 | Stamens 10, diadelphous – 9 stamens unite to form one bundle and 1 other bundle |
| A0 | Sterile stamen (staminode) |
| G0 | Sterile carpel (pistillode) |
| G- | Semi inferior ovary |
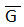 | Inferior ovary |
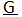 | Superior ovary |
How to Use Floral Formula?
Firstly, the presence or absence of bract and bracteoles in the flowers of different families is observed and noted by using particular letters.
Then the symmetry of the flower is written according to the position of floral whorls relative to the mother axis. Flowers can be polysymmetric (actinomorphic), dissymmetric, monosymmetric (zygomorphic), asymmetric or spirally arranged. Therefore, the flowers showing different symmetry is indicated by specific symbols in the floral formula.
After that, the sex of the flower is written, i.e. whether a plant is hermaphrodite (bisexual) or unisexual. Bisexual flowers possess the male plus female reproductive parts, while the unisexual flowers either contain stamens or carpels.
Then the number of floral members starting with calyx, corolla, androecium to gynoecium is written. Here each member is denoted by using specific letters like ‘K’ represents calyx, ‘C’ represents corolla, ‘A’ indicates androecium and ‘G’ represents gynoecium. The number of each whorl is written after the following letters starting from K, C, A to G.
The number used after the letter is placed inside bracket ( ), If the particular whorl is united. But, if the floral members remain free, then the bracket is not applied. Adnation between the floral whorls is represented by drawing a curve from the top of the letters.
The position of the ovary can be shown by drawing a horizontal line above, below or in front of the letter ‘G’, which represents the inferior, superior or half inferior position of the ovary.
Examples
The floral formula can be used to describe the flowers of the particular family or the different species of flower. Let us take few examples of the floral formula to study the floral characteristics.
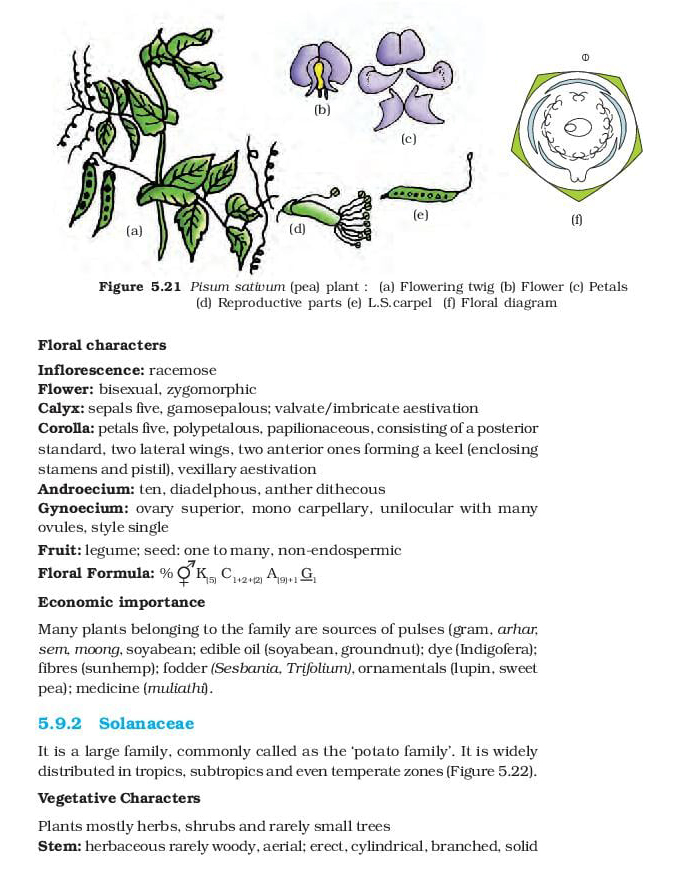
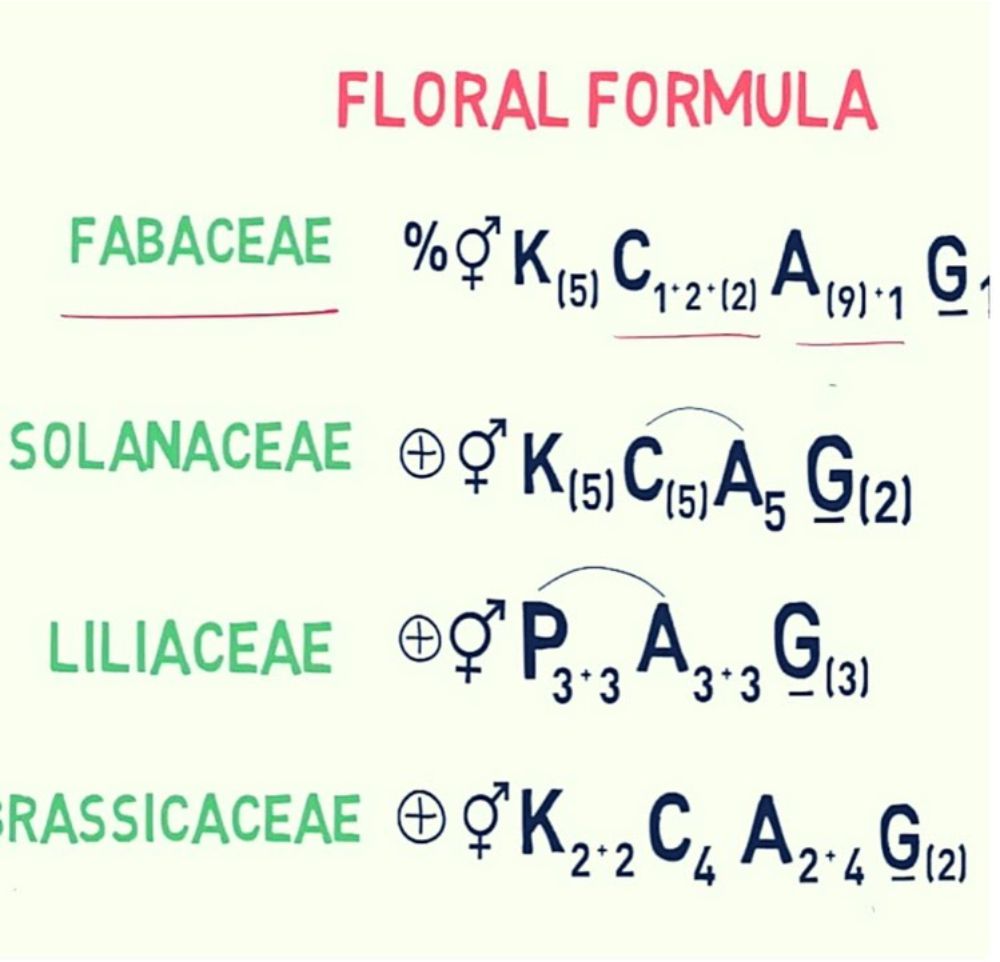
Floral Formula of Fabaceae Family
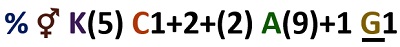
(%) shows that the symmetry of the flower is monosymmetric or zygomorphic. (⚥) indicates that the flower is perfect or hermaphrodite (includes stamen plus pistil). A letter ‘K’ indicates the outermost whorl, i.e. calyx and (5) shows that the number of sepals is five that are united with each other.
‘C’ indicates the second floral whorl, i.e. corolla or petals and the number after this, i.e. 1+2+(2), represents vexillary aestivation. ‘A’ means the male reproductive part or androecium, and the number after it (9)+1 shows the presence of diadelphous stamens (includes 10 stamens).
In 10 stamens, 9 filaments unite to constitute one bundle, and the remaining one filament makes up another one. The line below the letter ‘G’ indicates the superior position of an ovary, and digit 1 shows the monocarpellary ovary.
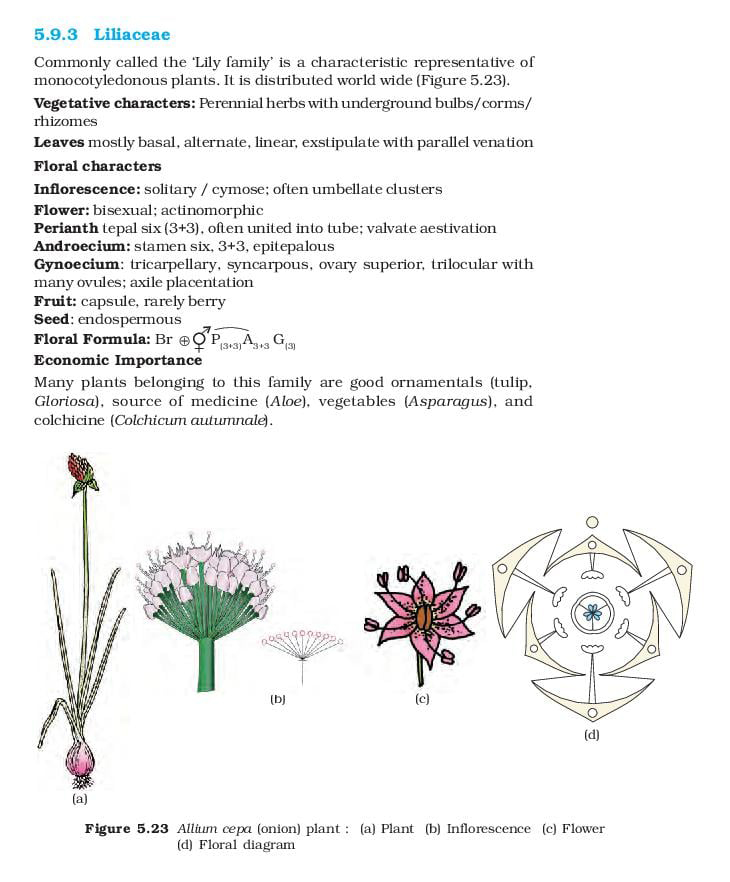
Floral Formula of Liliaceae Family
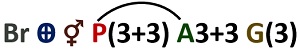
Through this floral formula, we can identify many floral characteristics. This formula indicates that the flower is bracteate, bisexual or hermaphrodite. A letter ‘P’ indicates that the sepals and petals are undifferentiated, i.e. there are three tepals in every two whorls.
Letter ‘A’ denotes androecium, and ‘3+3’ suggests there are three free stamens in every two whorls. A line below a letter ‘G’ specifies the hypogynous condition of an ovary, and the number ‘(3)’ represents the presence of three fused carpels.
Floral Formula of Solanacae Family
The general floral formula of Solanaceae family is as follows:
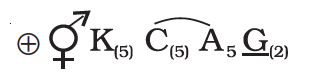
Here the symbols represent:
| ⊕ | Actinomorphic (radial symmetry) |
| ⚥ | Bisexual |
| K(5) | Calyx – 5 sepals, gamosepalous (united) |
| C(5) | Corolla – 5 petals, gamopetalous |
| A5 | Androecium – 5 stamens, polyandrous (free), epipetalous (attached to petals) |
| G(2) | Gynoecium – bicarpellary, syncarpous (united), superior ovary |
- Calyx (K): Composed of 5 sepals, which are united (gamosepalous).
- Corolla ©: Consists of 5 petals, which are also united (gamopetalous).
- Androecium (A): Contains 5 stamens, which are free (polyandrous) and attached to the petals (epipetalous).
- Gynoecium (G): Bicarpellary (two carpels), syncarpous (united), and has a superior ovary.
The Solanaceae family includes a variety of plants, such as potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers, eggplants, and tobacco. These plants exhibit diverse characteristics and are widely distributed across tropical, subtropical, and temperate zones.
Fabaceae floral formula

Take Quiz
1. NEET 2021 QP
Match Column – I with Column – II
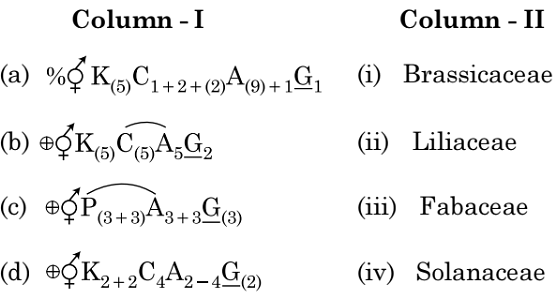
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
- (a)-(iv), (b)-(ii), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
- (a)-(iii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i)
- (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
- (a)-(ii), (b)-(iii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i)
ANSWER
b) (a)-(iii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i)
Fabaceae: The flowers in Fabaceae exhibit zygomorphic symmetry and are bisexual. The calyx is composed of five fused sepals, while the corolla is papilionaceous, consisting of one standard petal, two wing petals, and two fused keel petals. The stamens are diadelphous, and the gynoecium is monocarpellary with a superior ovary.
Solanaceae: Solanaceae flowers are actinomorphic and bisexual. The calyx features five fused sepals, and the corolla consists of five fused petals. There are five epipetalous stamens, and the gynoecium is bicarpellary and apocarpous with a superior ovary.
Liliaceae: Liliaceae flowers are actinomorphic and bisexual. The perianth comprises six fused tepals, arranged in two rows. There are six epipetalous stamens, and the gynoecium is tricarpellary and syncarpous with a superior ovary.
Brassicaceae: Flowers in Brassicaceae exhibit actinomorphic symmetry and are bisexual. The calyx consists of four sepals arranged in two rows (polysepalous), while the corolla comprises four petals (polypetalous). There are six stamens, arranged in two rows (tetradynamous), and the gynoecium is bicarpellary and syncarpous with a superior ovary.
So, the correct option is (B): (a)-(iii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i)
2) Floral formula below belongs to which family?
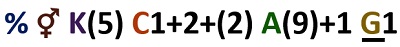
- Solanaceae
- Liliaceae
- Fabaceae
- Brassicaceae
ANSWER
c) Fabaceae
(%) shows that the symmetry of the flower is monosymmetric or zygomorphic. (⚥) indicates that the flower is perfect or hermaphrodite (includes stamen plus pistil). A letter ‘K’ indicates the outermost whorl, i.e. calyx and (5) shows that the number of sepals is five that are united with each other.
‘C’ indicates the second floral whorl, i.e. corolla or petals and the number after this, i.e. 1+2+(2), represents vexillary aestivation. ‘A’ means the male reproductive part or androecium, and the number after it (9)+1 shows the presence of diadelphous stamens (includes 10 stamens).
In 10 stamens, 9 filaments unite to constitute one bundle, and the remaining one filament makes up another one. The line below the letter ‘G’ indicates the superior position of an ovary, and digit 1 shows the monocarpellary ovary.
3) Which of the following is false about floral formula –
- Indefinite number of floral parts is shown with the help of infinity symbol ‘∞’
- Calyx is denoted with the letter ‘C’
- K5 means there are five petals, aposepalous
- A2+2 means 4 free stamens, two in each whorl
ANSWER
b) Calyx is denoted with the letter ‘C’
In the floral formula, calyx (sepals) is denoted as ‘K’ and not ‘C’. it is one of the non-essential organs of the flower, it is the outermost and the first whorl of the flower. In the bud stage of the flower the calyx forms a protective layer around the bud. The ‘C’ in the floral formula is written for corolla.
K5: It shows the aposepalous condition, in which the five sepals are free.
K(5): It shows the gamosepalous condition, in which the five sepals are united.
C5: It represents the apopetalous condition or the presence of the five free petals.
C(5): It represents the gamopetalous condition or the presence of five fused petals.
4) The correct floral formula of soyabean is (NEET 2010 QP)
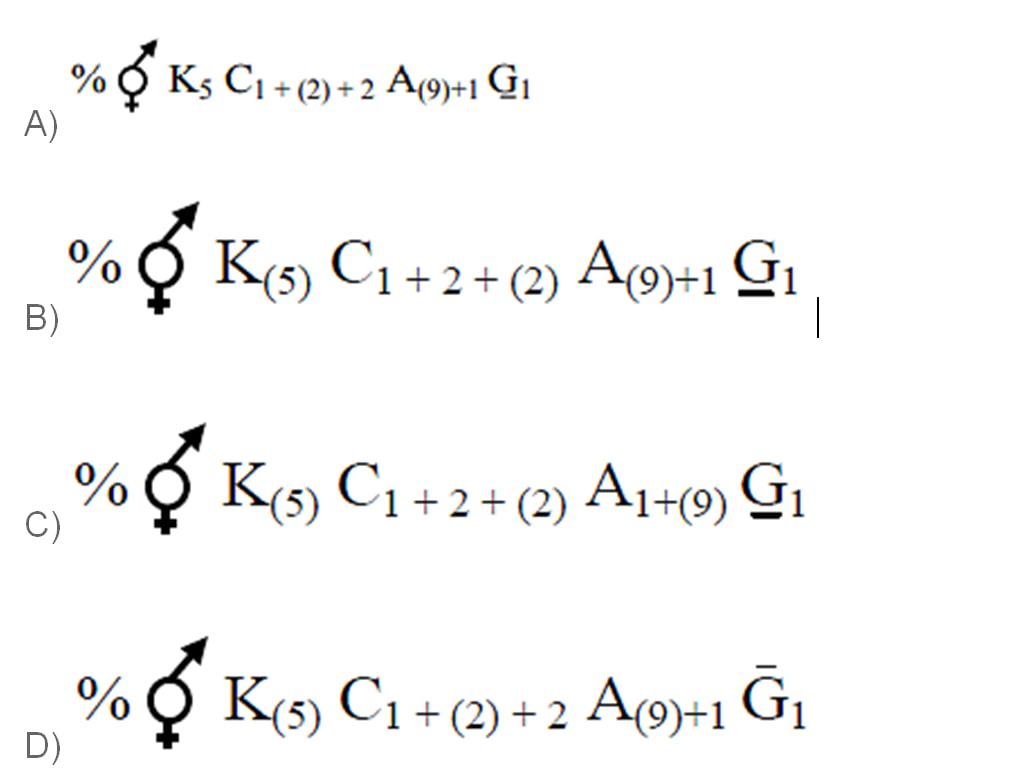
ANSWER
The plants belonging to the family fabaceae such as soyabean, pea, moong, gram, etc have the floral formula
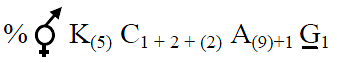
5) NEET 2016 QP
Tricarpellary, syncarpous gynoecium is found in the flowers of
(a) Liliaceae
(b) Poaceae
(c) Fabaceae
(d) Solanaceae
ANSWER
a) Tricarpellary, syncarpous gynoecium is a unique reproductive structure found in the flowers of Liliaceae family. It is formed by the fusion of three carpels, resulting in a single, compound ovary with three chambers. Each chamber has its own style and stigma, which are designed to facilitate pollination and fertilization.
