Table of Contents
Interactions and Relationship
Lessons from class 12
Commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are the three main categories of symbiosis found in nature.
Commensalism
In a commensal relationship, one species benefits and there is a neutral effect on the other—it neither benefits nor is harmed.

- Sucker fish attaches to shark fish with the help of dorsal fin feeding on the falling pieces of food and shark does not get any benefit from it therefore, this interaction is Commensalism.
- Barnacles benefiting from having a place to settle and filter food, while the whales do not seem to suffer any negative consequences from their presence.
Other examples of commensalism are
- Spiders spinning webs on plants
- Hermit crabs that use discarded snail shells to protect themselves.
- An orchid growing on the branch of a mango tree is an epiphyte. Epiphytes are plants growing on other plants which, however, do not derive nutrition from them.
- Burdock seeds on animals- Burdock seeds get attached to the animals and are transported to various places on their back. This helps them to spread in the land. Burdock seeds are very light that animals barely experience their presence.
When commensals dwell on the host’s body, using it as their habitat, it is called Inquilinism.
Commensalism + /0

Mutualism (+/+)
In this type of symbiosis, both organisms benefit from the relationship.
A classic example of this is the relationship between termites and the protists that live in their gut. The protists digest the cellulose contained in the wood, releasing nutrients for the benefit of the termite. In turn, the protists receive a steady supply of food and live in a protected environment.
Other examples of mutualism are the algae that live in the tissues of coral in reefs, clownfish that live in the tentacles of sea anemones, in which the anemone protects the clownfish against predators, while the clownfish provides the anemone with excreted nutrients (ammonia, sulfur, and phosphorus).

- The relationship between the Oxpecker bird and Buffalo where bird eats the insects on the skin of buffalo while the buffalo gets rid of the ticks and insects.
- Zebras and rhinoceroses on the African plains.
- Lichen representing mutual association between algae and fungi, in which algae is protected by fungi. The fungi provides nutrients for synthesis of food to the algae, while algae provides food to fungi, as they are incapable of synthesising their own food.
- Aphids are little sap-sucking insects that secrete honeydew, a sugary liquid that is the waste product of their diet. Many aphid species are known to engage in a mutualistic relationship with ants that feed on the honeydew. In return, some species of ants will protect the aphids from predators and parasites.
- The corals and algae relationship. The coral provides shelter and essential nutrients for the zooxanthellae to use during photosynthesis, while the zooxanthellae produce synthetised sugars, which the coral feeds on, and oxygen as a by-product.
- Another example is monkeys and fruit-producing trees. The monkeys’ benefit by eating the fruit, and the trees benefit from the monkeys carrying the seeds away as a method of seed dispersal.
Parasitism (+/-)
Parasitism is a relationship where one symbiont benefits (the parasite) and the other (the host) is harmed in some way.
Parasitism is the type of symbiotic relationship or long-term relationship between any two species either plants or animals. Here the parasite gains benefits from the host which in turn harms the host without killing it.

-
- External Parasites (Ectoparasite) Leeches (Hirudinea), fleas, ticks, and lice are a few examples of parasites that don’t normally cause disease directly. They suck blood from the host without causing any harm to their host.
- There are different species of Plasmodium that are picked up by the mosquitoes and transmitted to different people causing Malaria.
- Tapeworm/ Teania solium can live in the human gastrointestinal tract for years. It spreads through under-cooked pork. These are more than three meters long.
- Fasciola Hepatica is an endoparasite that affects Liver. Internal parasites show more extreme specialization and have a less complex structure.

Amensalism (-/0)
Amensalism is a biological interaction between two species in which one is inhibited or destroyed and the other is unaffected.
There are two basic modes:
competition, in which a larger or stronger organism excludes a smaller or weaker one from living space or deprives it of food. For example, the black walnut tree produces a chemical called juglone that inhibits the growth of many plants beneath it.
Antibiosis, in which one organism is destroyed by metabolic products of another. An example of antibiosis is the interaction between Penicillium and bacteria. The mould Penicillium creates the secretion known as penicillin, which is extremely toxic to bacteria.

Predation (+/-)
In this relationship, one organism kills and eats the other. Examples include a jaguar killing and eating a tapir as well as horses eating grass. Unlike parasitism, where the host remains alive while the parasite lives off it, predation results in the death of one of the organisms.

Population of predator is generally small because if predator is too efficient or too many in number, they may over exploit its prey which may extinct and following it, predator will also extinct so, predator checks the population of prey but do not extinct them.
The predator population works according to the prey and help in keeping the prey population in a check. In absence of predators, the population will increase immensely and will affect the normal ecological balance, so they respond functionally.
Competition (-/-)
Competition is when two organisms both want the same limited resource. Because they have to compete for the resource (often food, water, or territory), both organisms are negatively impacted.
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resources in an ecosystem (e.g. food or living space).
Competition between members of the same species is called intraspecific competition.
Cheetahs and lions both attempting to hunt the same small herd of zebras is an example of competition. If there aren’t enough zebras for both animals to eat, they will both get less food than what they want and may suffer from hunger/starvation as a result.
In interspecies competition, two species use the same limited resource. Competition has a negative effect on both species. Mostly it occurs when there is a limited resource, and two species are trying to accommodate. This competition has adverse effects on all species utilizing a similar and limited resource at the same time and place making them smaller in population size.
Plant -animal interactions often involve co-evolution of the muralists, that is, the evolution of the flower and its pollinator species are closely linked, with one another. It occurs in mutualism and parasitism where one species is close relationship with the other.
- Gause’s law of competitive exclusion or just Gause’s law is a proposition that states that two species competing for the same resource cannot coexist at constant population values if other ecological factors remain constant.
- When two competing life forms attempt to occupy the same niche, only one outcome is possible: One life form will drive out the other.
Symbiosis interaction Chart:
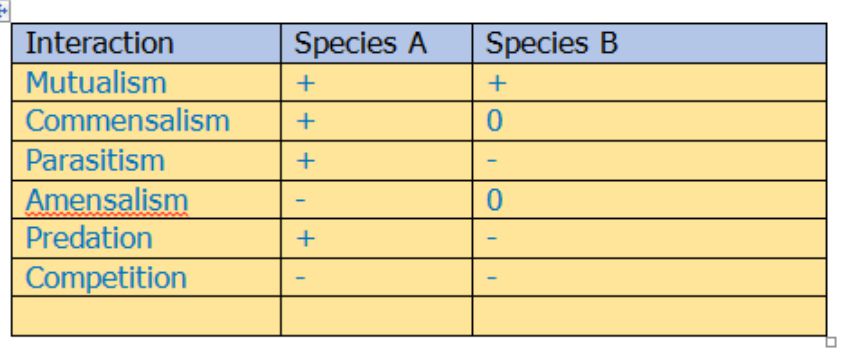
Quick Quiz:
1) What is an interaction called when an orchid grows on a mango plant?
The relation between a mango tree and an orchid is commensalism. An orchid growing on the branch of a mango tree is an epiphyte. Epiphytes are plants growing on other plants which, however, do not derive nutrition from them.
A.
2) A Tight one-to-one relationship between many species of fig tree and certain wasps is an example of (a) Commensalism (b) Parasitism (c) Amensalism (d) Mutualism
B. The relation between a mango tree and an orchid is commensalism. An orchid growing on the branch of a mango tree is an epiphyte. Epiphytes are plants growing on other plants which, however, do not derive nutrition from them.
C.
3) The effect of interspecific competition on niches is to make them? a) Smaller b) Larger c) Change location
D. In interspecies competition, two species use the same limited resource. Competition has a negative effect on both species. Mostly it occurs when there is a limited resource, and two species are trying to accommodate. This competition has adverse effects on all species utilizing a similar and limited resource at the same time and place making them smaller in population size.
E. So, the correct answer is ‘Smaller’.
II. 4) Co-evolution can be observed in case of :
Plant -animal interactions often involve co-evolution of the muralists, that is, the evolution of the flower and its pollinator species are closely linked, with one another. It occurs in mutualism and parasitism where one species is close relationship with the other.
5)In a population of predator and prey it was seen that when the prey population was numerically high the predator population consumed more and more prey. This is because the predator population
A) Can digest any amount of food.
B) Responds functionally.
C) Responds numerically.
D) Is a voracious feeder.
The predator population works according to the prey and help in keeping the prey population in a check. In absence of predators, the population will increase immensely and will affect the normal ecological balance, so they respond functionally.
So Ans is Option B) Respond functionally
The principle of competitive exclusion was stated by
1. Mac Arthur
2. Verhuslt and Pearl
3. Darwin
4. G. F Gause
Gause grew populations of Paramecium aurelia and the larger P. caudatum, in controlled conditions. When these two populations were grown in separate test tubes, the population of each species quickly increased to the carrying capacity. When grown together, determined by available conditions, one species thrived over other. It led to the principle of competitive exclusion that two competing species cannot coexist and in time one or the other would eventually out-compete.
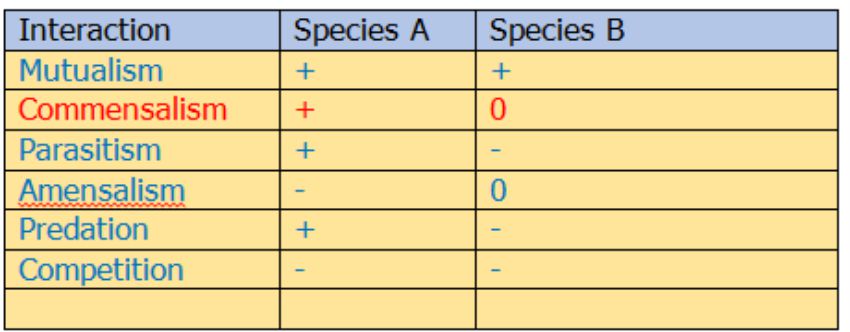
(+ )(0)–Relationship sign shown by
a) Amensalism b) Predation c) Commensalism
Ans: Option C) Commensalism
Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023 question)
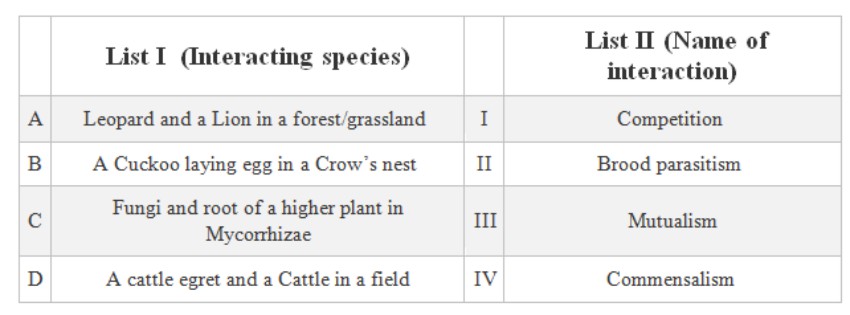
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
- A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
- A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
- A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
- A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
Ans: option D) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
Match List I with List II: (NEET 2023 Question)
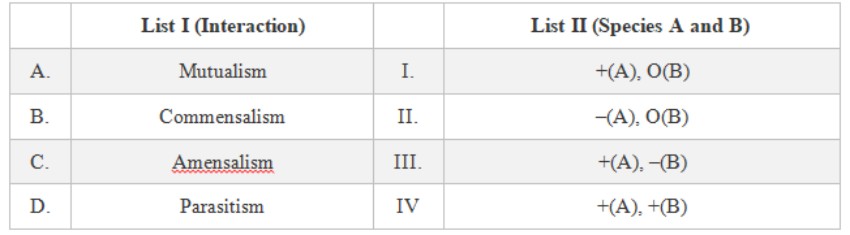
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-II
- A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
- A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
- A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
Ans: Option A) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-II
